Allowing you to test applications at scale regardless of platform — including z/OS.
Project Overview:
Galasa is an open source deep integration test framework designed for agile, reliable, and scalable testing across various technologies and platforms. By supporting consistent testing without code changes, enabling multi-technology integration, and providing efficient test data management, Galasa enhances DevOps strategies.
Galasa centralizes test results, simplifies test planning, and offers extensibility without vendor lock-in. With a focus on hybrid cloud testing and seamless integration into CI/CD pipelines, it empowers organizations to achieve faster, more comprehensive software testing and delivery.
Automated testing and agile delivery are traditionally seen as being available only in greenfield projects, but with the introduction of Galasa, you can be agile in a mainframe environment as well.
Using Galasa in a hybrid cloud environment
Using hybrid cloud, enterprises can host applications and data on the platforms that deliver the best combination of efficiency, security, and performance. However, a mix of platforms and technologies makes end-to-end integration testing complicated.
Galasa simplifies testing in such an environment. The following diagram shows an example of how you can use Galasa to test a hybrid cloud application:
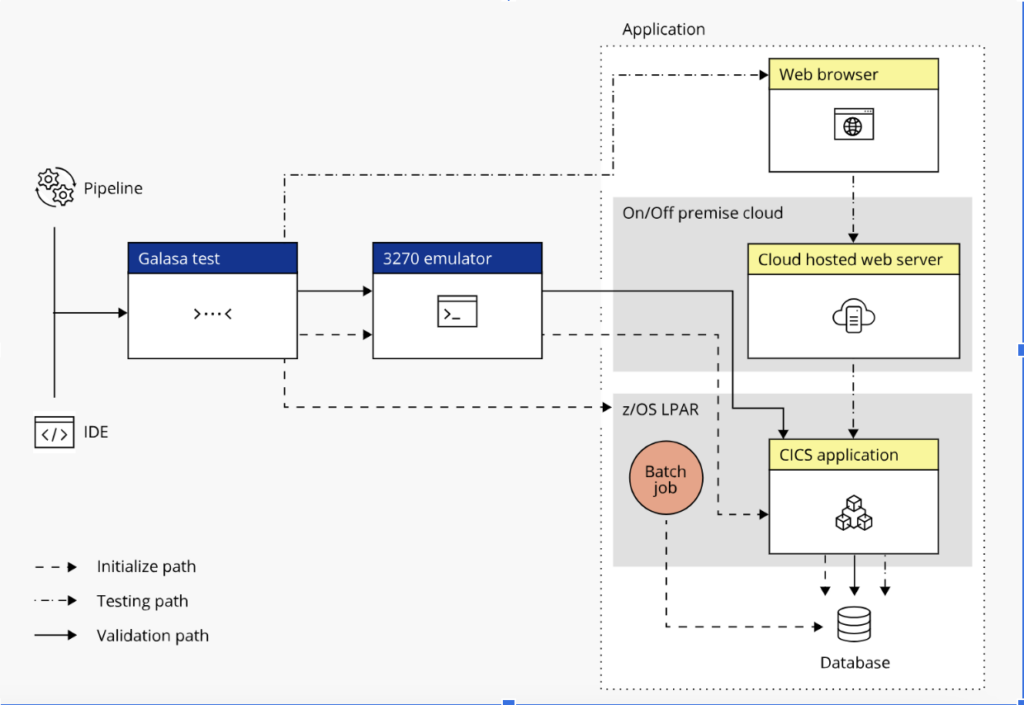
This sophisticated solution requires end-to-end integration testing of an application that runs on different platforms (z/OS and Cloud) and uses different technologies (a 3270 emulator, JCL batch job and Selenium Web Driver).
When run inside a Galasa ecosystem, a Galasa test can be invoked from an IDE or as part of a CI/CD pipeline. The Galasa framework initializes the test environment, creates valid test data, runs the test and validates the test output. As all test results and artifacts are stored in one location, it’s easy to generate reports and diagnose the cause of any failures.
Testing without limitations
Testing an endpoint, whether it be a 3270 terminal, a REST API or a web service is a simple operation and there are plenty of tools that enable you to accomplish this task. However, there are limitations to some of these tools:
- The tests cannot utilize a mix of technologies. For example, let’s say you need to examine an IBM CICS or a z/OS resource to validate that the response from the REST endpoint you are testing is correct. How can the test get this information without the tester understanding how to access it?
- Most of the tools require some level of manual operation which limits their effectiveness in a continuous delivery pipeline.
- The tools cannot contextually bind to either a provisioned, or pre-existing environment in an intelligent manner.
Galasa makes it simple for a test to access, drive and interrogate a range of z/OS, distributed and open source tools and integrate them together within the same simple test class.
Tests written for Galasa can be run locally on your computer for manual debugging or can be scheduled to run on a server in automation mode – great for overnight runs or when you need to run tests in parallel or at scale.
Key benefits of using the Galasa test framework
Smooth integration with the rest of your pipeline:
- A single API runs any test regardless of underlying technology.
- Tests can be dynamically selected from a catalog.
- Environment stability is assured before tests are run.
- Test results can be monitored automatically.
A single point of control:
- Test artifacts are centrally stored and indexed.
- Test results are correlated, ensuring the quality of the release for all product components.
- This is a single control for allocation and management of resources and tests.
Scalable testing:
- Late binding of the test material to the system under test allows the same test to run against multiple environments without changing the test.
- Tests scale horizontally without changing the underlying test code.
- Management of test isolation means that multiple tests can run in parallel, logically isolated by the framework.
Environment-agnostic capabilities:
- Tests can be run against multiple environments as code progresses through release stages.
- The Galasa test engine allows tests to run locally for easier development and debugging, as well as in the Galasa ecosystem for production testing at scale.